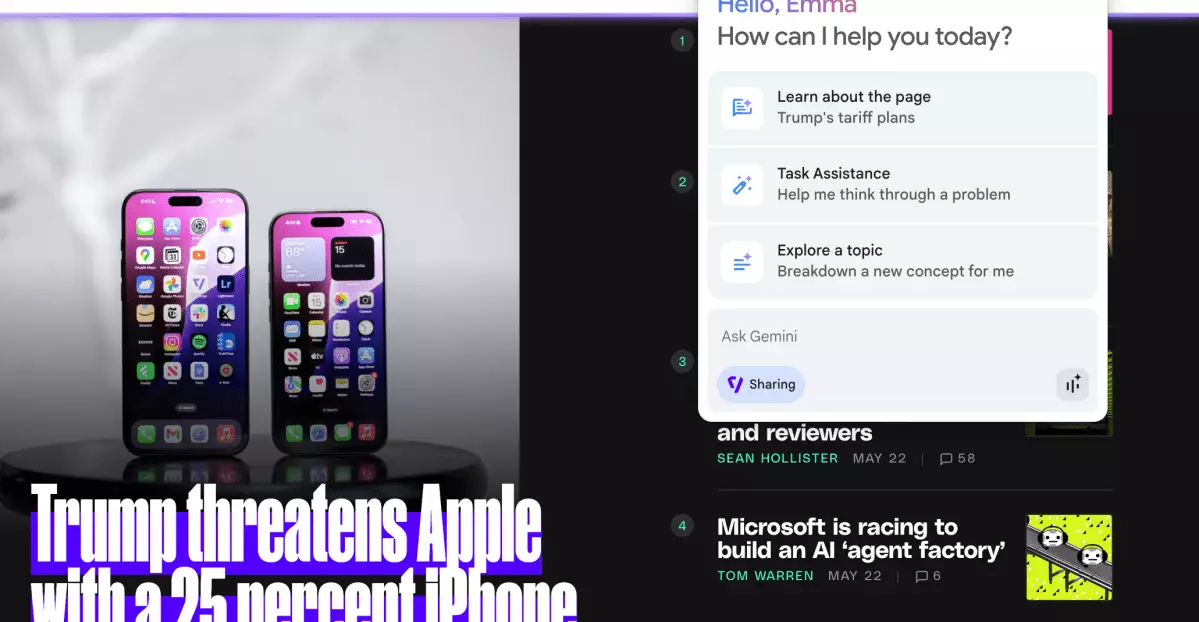
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, the introduction of AI-driven tools has the potential to revolutionize how we navigate the web. Chrome’s latest integration with Gemini, Google’s sophisticated AI assistant, marks a pivotal moment in merging user experience with advanced technology. This innovation not only promises to enhance productivity but also aims to redefine the way users interact with information online.
Gemini transforms the traditional browsing experience by embedding AI capabilities directly into the chrome environment. Users can access this powerful tool with just a click, allowing the assistant to “see” what’s on their screens. This feature provides a distinctly different flair compared to conventional web apps, making Gemini a game-changer for daily browsing activities.
Streamlined Information Gathering
At its core, Gemini is designed to enhance information retrieval. For example, during a trial with Gemini while browsing The Verge, it summarized articles and identified relevant gaming news effortlessly. The AI pointed out updates on the Nintendo Switch Online service, including new Game Boy games—a task that can often be tedious for the average user. However, Gemini’s limitations became apparent during these interactions; it could only provide insight from one tab at a time, and the efficacy of its summaries often depended on the visibility of content on the screen.
This limitation raises questions about how deeply integrated AI can be in an existing browser environment. The idea of an increasingly “agentic” AI holds promise, but current functionality leaves much to be desired. Users are likely to look for a more fluid experience where the assistant can cater to multiple tabs and sources simultaneously—attributes that would significantly elevate its utility.
Enhancing Learning Through Voice Interaction
One of the standout features of Gemini is its speech recognition capabilities. Switching to the “Live” mode allows users to pose questions verbally, which is particularly advantageous during activities like watching instructional YouTube videos. The AI adeptly identified tools and summarized content that may not have been directly visible, showcasing its potential as a hands-free support system. It responded promptly and accurately in many instances, such as noting a nail gun being used in a renovation project. This level of interaction not only makes Gemini practical but also enhances learning experiences in real time.
However, this AI is not without its faults. There were moments when it failed to deliver precise answers regarding real-time information, such as identifying the current whereabouts of a popular YouTuber. The inconsistency in these moments highlights the considerable challenges that remain in making AI as reliable as it is intended to be.
The Quest for True Agentic Functionality
While Gemini demonstrates significant capability in assisting with simple tasks like summarizing content or identifying objects, its limitations underline a broader challenge facing AI in fulfilling its intended role. Future developments, particularly through initiatives like Project Mariner’s “Agent Mode,” aim to push these boundaries further. This proposed upgrade would allow Gemini to manage multiple tasks simultaneously and conduct web searches independently—elements crucial for fulfilling more complex requests.
Yet, the current experience reveals a jarring contrast between expectation and reality. Users may anticipate a seamless interface, but Gemini’s tendency to deliver lengthy responses or repetitive follow-up questions detracts from its intended efficiency. In an age where speed is paramount, any lapse in succinctness can leave users feeling frustrated rather than empowered.
The Future of Browsing with AI Integration
As companies like Google aim to make AI more agentic, the potential applications are vast. Imagine a future where Gemini not only summarizes a restaurant’s menu but also places a pickup order based on user preferences. Such capabilities would eliminate manual tasks, streamline the user experience, and potentially change how people interact with technology.
However, for these advancements to materialize, developers must prioritize enhancing the assistant’s reliability and responsiveness. Users may find it difficult to fully embrace AI integrations if basic functionalities continue to falter. Efforts should be aimed at refining Gemini to ensure that it delivers information that is not only accurate but also concise, keeping the browsing experience fluid and efficient.
Overall, the incorporation of Gemini into Chrome is just a hint of what the future holds. As Google refines and expands its AI capabilities, it is clear that the blending of browsing and artificial intelligence is on the horizon. Embracing these technologies with a critical eye will be essential in shaping an enhanced, intelligent web experience, making the digital landscape more user-friendly and accessible than ever before.